Frame & Chassis
What is a Chassis?
The chassis of a vehicle is the load-bearing part of the frame, - consists of engine, power train, brakes, steering system and wheels mounted on a frame - which in turn is the structural element of the body of the car
Functions of Chassis
- Limiting body roll under cornering.
- Improving a car’s ability to navigate corners and uneven terrain.
- Helping with the noise, vibrations and harshness (NVH) levels.
- Allowing efficient transfer of power from the engine to wheels.
- To act as a foundation or a base for key components like the suspension, the body, the wheels and the tires.
Types of Chassis
- [[#Ladder Frame Chassis]]
- [[#Backbone Chassis]]
- [[#Tubular/ Spaceframe Chassis]]
- [[#Monocoque Chassis]]
- [[#Electric Vehicle Chassis]]
Ladder Frame Chassis
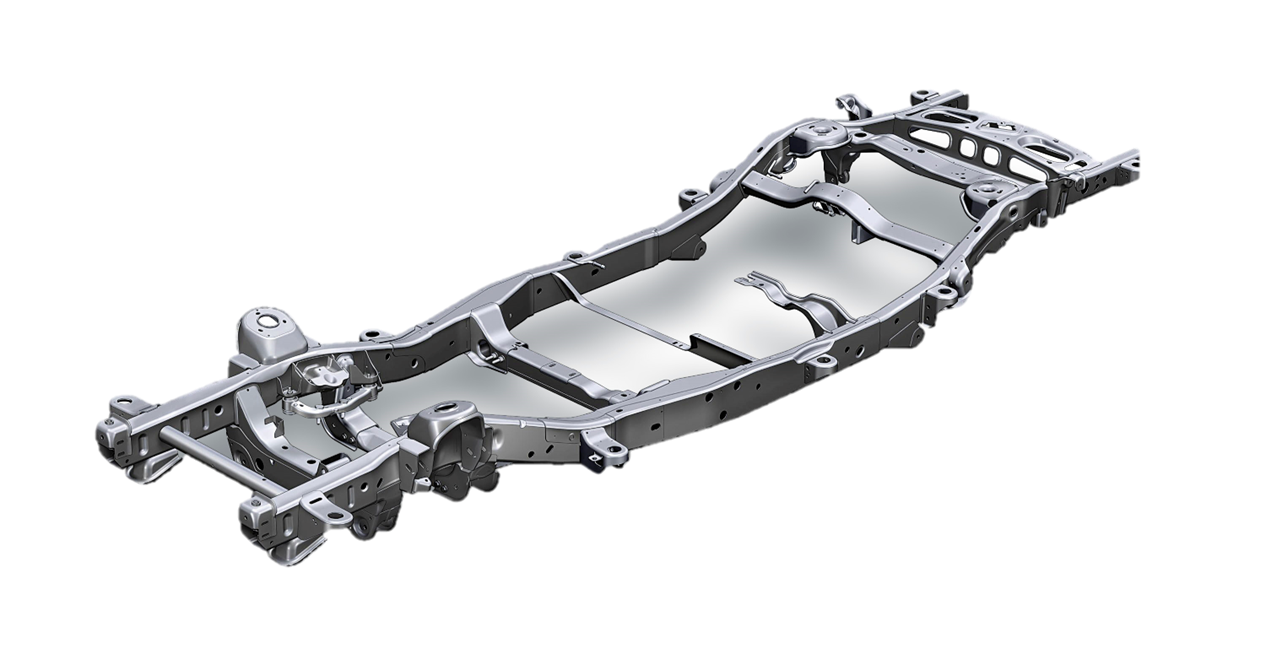

- As the name suggests, a ladder shaped structure is present here
- 2 parallel members are placed on the sides and cross members are used to join this chassis structure at various points
Pros
- Ladder frame chassis is easy to construct and assemble
- Provides the car with high structural integrity
- It is solid and suitable for bulky, load-carrying vehicles like trailers and trucks
Cons
- The ladder frame chassis is heavy, making it unsuitable for lightweight and high performance vehicles
- It exhibits weak torsional ability.
Examples
Toyota Fortuner, Mahindra Thar, Ford Endeavour, Force Gurkha, Mahindra Alturas G4, and Mercedes AMG G63
Backbone Chassis
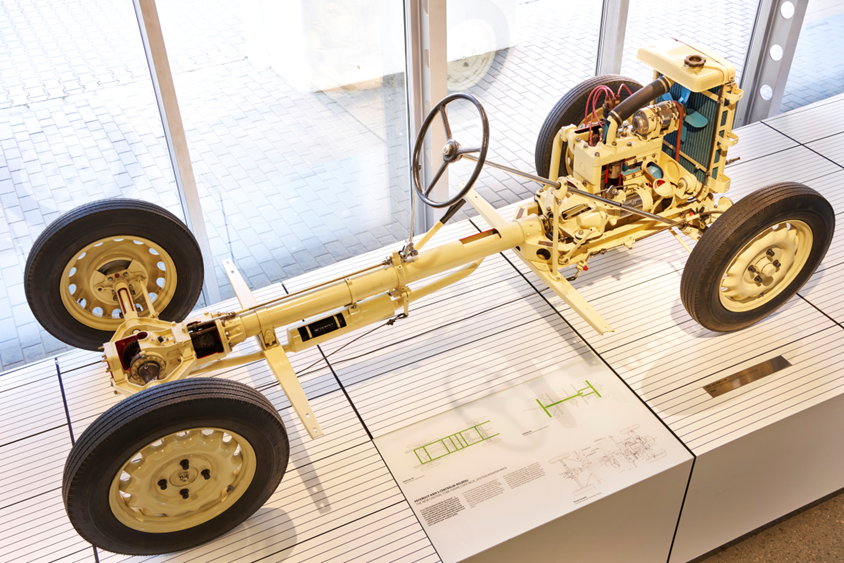
- The backbone chassis is sometimes called the central backbone or central tube design, as it resembles the human backbone.
- This chassis type features a hollow cylindrical tube connecting the front and rear axles and suspension.
- Due to its high torsional toughness, it is the go-to design for off-road vehicles.
Pros
- High torsional toughness
- The backbone chassis provides a strong and rigid foundation for the vehicle
- Excellent for off-road vehicles and passenger cars
Cons
- It attracts high manufacturing costs
- Issues with the driveshaft may compromise the entire vehicle’s chassis.
Examples
DMC DeLorean, Lotus Elan, Lotus Esprit
Tubular/ Spaceframe Chassis
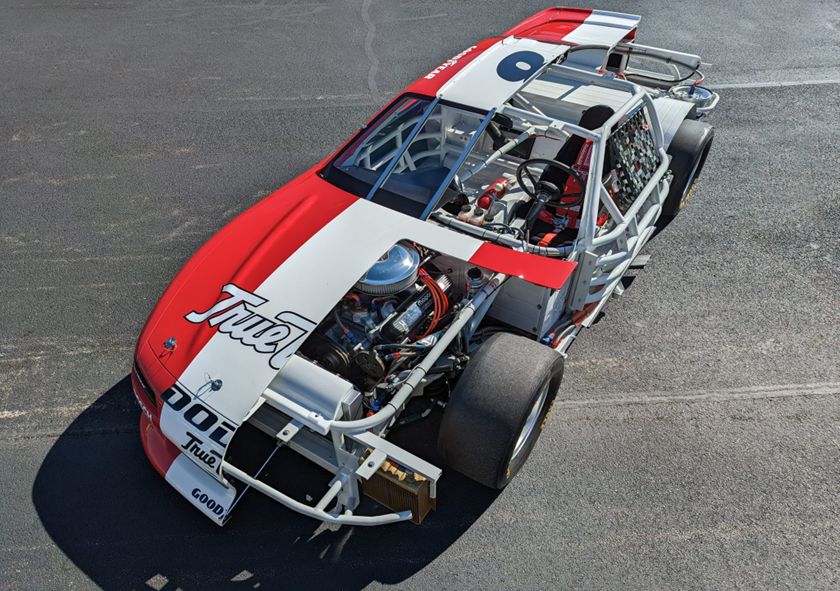

- Tubular chassis are also known as space car chassis frames, as they consist of a series of networks of tubular members, creating the three-dimensional structure that forms the car chassis.
- They are common in lightweight, high-performance, and race vehicles.
- Furthermore, the tubular chassis is the 3D representation of the conventional ladder frame chassis
Pros
- The tubular chassis offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and crash resistance
- Excellent for vehicles with lightweight specifications
- Allows for enhanced design flexibility and customization.
- Comparatively better rigidity for the chassis of the almost same weight
- Highly preferred for race cars
Cons
- It features a complex design, making construction challenging.
- They are very time-consuming in production, and can’t be mass-produced.
- Not suitable for passenger cars
- The tubular chassis elevates the doors a bit making it slightly hard to access the cabin
Examples
NASCAR racecars, Rally Cars
Monocoque Chassis
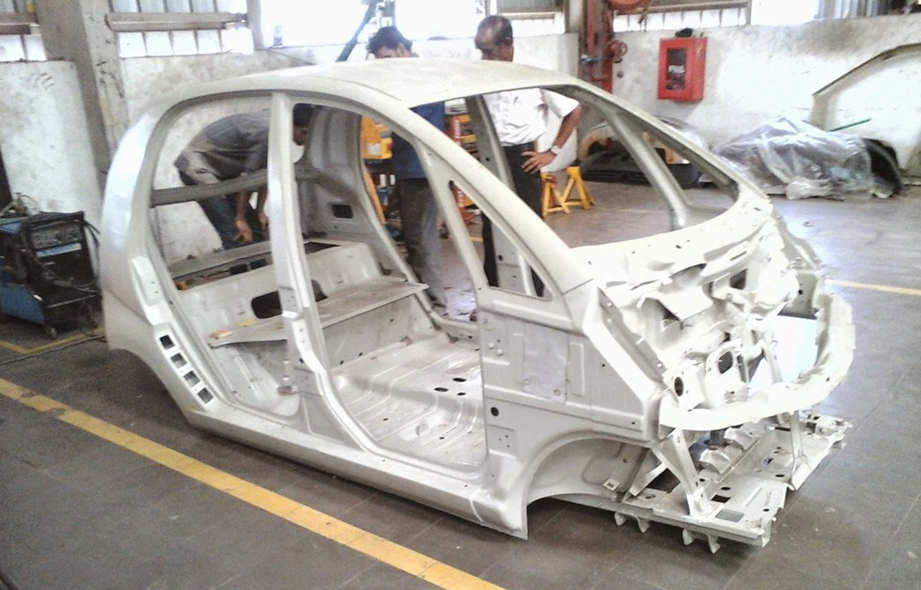

- The monocoque chassis design, also known as the unibody design, fuses the car frame and chassis into a single unit.
- It is the standard chassis type in most modern vehicles, including sedans, hatchbacks, and SUVs.
- Therefore, the monocoque chassis design goes beyond aesthetics; it provides exceptional strength, rigidity, and crash resistance.
Pros
- It provides high torsional rigidity;
- The fused design helps to protect its components, making it more durable
- The monocoque design helps to absorb and effectively distribute crash energy
Cons
- Because of the fusing with the car frame, monocoque chassis is expensive to manufacture;
- The fused design may make repairs difficult.
Examples
Tata Nano, Toyota Fortuner, Hyundai Verna & almost all passenger vehicles on sale today
Electric Vehicle Chassis
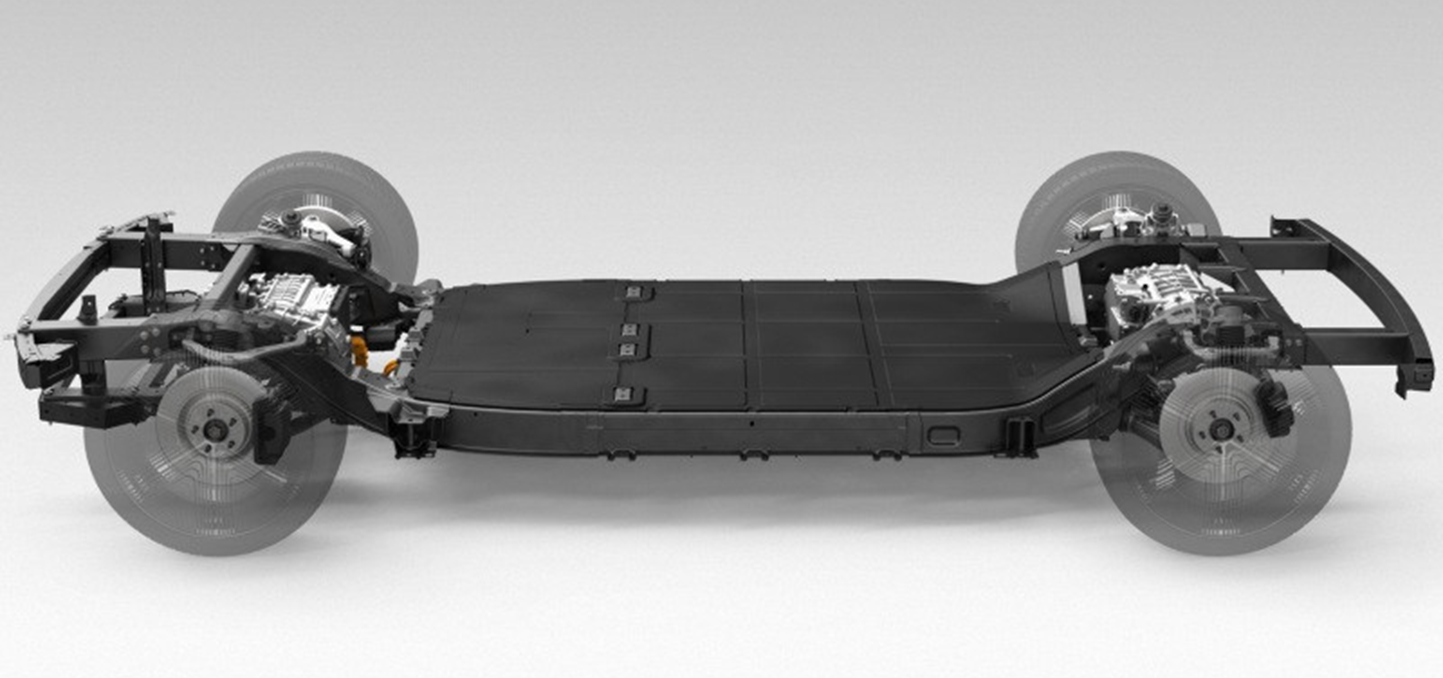
- Electric vehicles too have chassis similar to the monocoque design, usually with a key alteration to the floor.
- In the case of EVs though, their chassis are commonly referred to as ‘skateboards’.
- This is because they resemble a long, low structure with four wheels, upon which the rest of the vehicle is built.
- The skateboard houses the batteries and the motors are located in or near the wheels.
- Also, they were designed to not only bear punishment and vibration thrown at them from the road, but also from naturally imbalanced internal combustion engine (ICE) that is bolted onto them.
- Not to forget the fast rotating transmission parts like gearbox, transfer shafts, differential, couplings were adding to this.
- Thus these chassis are strong and rigid enough to take all this abuse and have special vibration dampening resilient mountings welded onto them for various components, which adds up their weight and cost as well.
Pros
- Carry large battery packs much lower down within the center of the chassis which lowers the center of gravity
- Aids in handling and stability of the vehicle and spreads even traction on all wheels
- Design conceals the battery pack within the rigid side beams of the chassis for better crash protection
- Frees up space inside cabin for passenger and luggage - the frunk and trunk
Cons
- Heavier chassis structure
- Needs a complete redesign & overhaul of suspension, braking, drivetrain systems to account for the vastly different vehicle dynamics and loading, in comparison to ICE
- Additional bracing & stiffeners for the battery pack
Examples
Tesla Model X, GMC Hummer, Nissan Leaf
Chassis vs Frame vs Platform
| Chassis | Frame | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| The chassis of a vehicle is the load-bearing part of the frame, - consists of engine, power train, brakes, steering system and wheels mounted on a frame - which in turn is the structural element of the body of the car. | A vehicle frame, is the main supporting structure of a motor vehicle to which all other components are attached, comparable to the skeleton of an organism. Chassis is a part of frame Until the 1930s, virtually every car had a structural frame separate from its body. This construction design is known as body-on-frame. |
By standardizing certain features of a vehicle, expenses can be minimized, as well as the time it takes to release a finished product onto the market. A platform includes many components, only one of which is the chassis. In addition to it, components such as the frame, suspension, drive unit, exhaust system or transmission can be standardized. |
Modular Vehicle Platform
- Includes chassis, drivetrain, steering, and suspension design
- Basic and flexible
- Shared among different vehicles
- Starting point for the rest of vehicle design
- Different bodies and variants added afterwards
Pros
- Single production line
- Lowers manufacturing costs
- Uniform parts and easier design
Did
Vehicle recalls have been growing in recent years due to new technologies and cost-cutting.
Cons
- More vehicles recalled in the event of a defects
- Could reduce brand differentiation
- Must comply with different regulations
Why are Modular Chassis adaptable?

- To become longer, shorter, wider, or narrower
- To fit different battery sizes
- To support gasoline, hybrid, and electric drivetrains